Pierre Sermanet
Co-founder & Chief Scientist @ UMA
Formerly Research Scientist @ Google DeepMind
Machine Learning for Robotics / Vision / Language / Actions / Safety
Selected highlights
2025
100k citations across machine learning, computer vision, and robotics
+ Laws of robotics generated from images and sci-fi
+ CVPR Prize for 10-year significant impact on computer vision by GoogLeNet paper
2023
Open-sourced large-scale VQA benchmark for robotics and developped embodied long-horizon reasoning
2020
First manipulation VLA: end-to-end Vision-Language-Action models for robotic manipulation and learned from unstructured play videos and very few labels
2017
Fully self-supervised imitation from video → robot policy learned without any labels
2016
Founding member of Google Brain Robotics team
+ Unsupervised rewards from vision
2014
Winner of Dogs vs Cats and 2014 ImageNet competitions
+ Joined Google Brain
2013
PhD graduation with Yann LeCun @ New York University
+ Open-sourced one of the first deep vision models (OverFeat)
+ Winner of 2013 ImageNet competition
2010 - 2012
ConvNets for detection, classification and unsupervised representations
2009
Designed and released an early open-source deep learning framework (EBLearn)
2006
Proposed a fast & slow thinking architecture for robotics (system 1 / system 2)
2005
Deep learning for robotics in DARPA’s LAGR program
Selected Projects and Publications (Full List)

SciFi-Benchmark: Leveraging Science Fiction To Improve Robot Behavior
Pierre Sermanet, Anirudha Majumdar, Vikas Sindhwani
Q: How would AI-powered robots behave if dropped into Science Fiction literature?
A: 95.8% aligned with humans (Sci-Fi decisions are only 21.2% aligned).
Q: Can we generate useful robot constitutions 📜 from Sci-Fi?
A: Sci-Fi inspired constitutions yield some of the strongest alignment on realistic safety benchmarks.

Generating Robot Constitutions
& Benchmarks for Semantic Safety
Pierre Sermanet, Anirudha Majumdar, Alex Irpan, Dmitry Kalashnikov, Vikas Sindhwani
Q: How can we ensure robots behave properly at scale?
A: Robot constitutions 📜!
Q: How do we verify behavior in undesirable situations at scale?
A: Generation!
We release the ASIMOV Benchmark for Semantic Safety of robots. We generate difficult-to-capture undesirable situations using image generation.
We also generate robot constitutions straight from images.
RoboVQA: Multimodal Long-Horizon Reasoning for Robotics
Pierre Sermanet, Tianli Ding, Jeffrey Zhao, Fei Xia, Yuan Cao et al. @ ICRA 2024, 2023 CoRL and NeurIPS workshops
Need help in the real world? RoboVQA can guide robots and humans through long-horizon tasks on a phone via Google Meet.
We propose scalable real-world data acquisition and augmentation strategies and release a dataset of 800k (video, question/answer) with robots & humans doing various long-horizon tasks.
We train a small video model (380M) that outperforms large state of the art zero-shot models by ~2x and demonstrate that scalable strategies for acquiring new data remains criticial.
We use a speech intervention mechanism that automatically quantifies progress (intervention rate), provides corrections to retrain on, and allows performing tasks to completion in supervised real-world deployment.
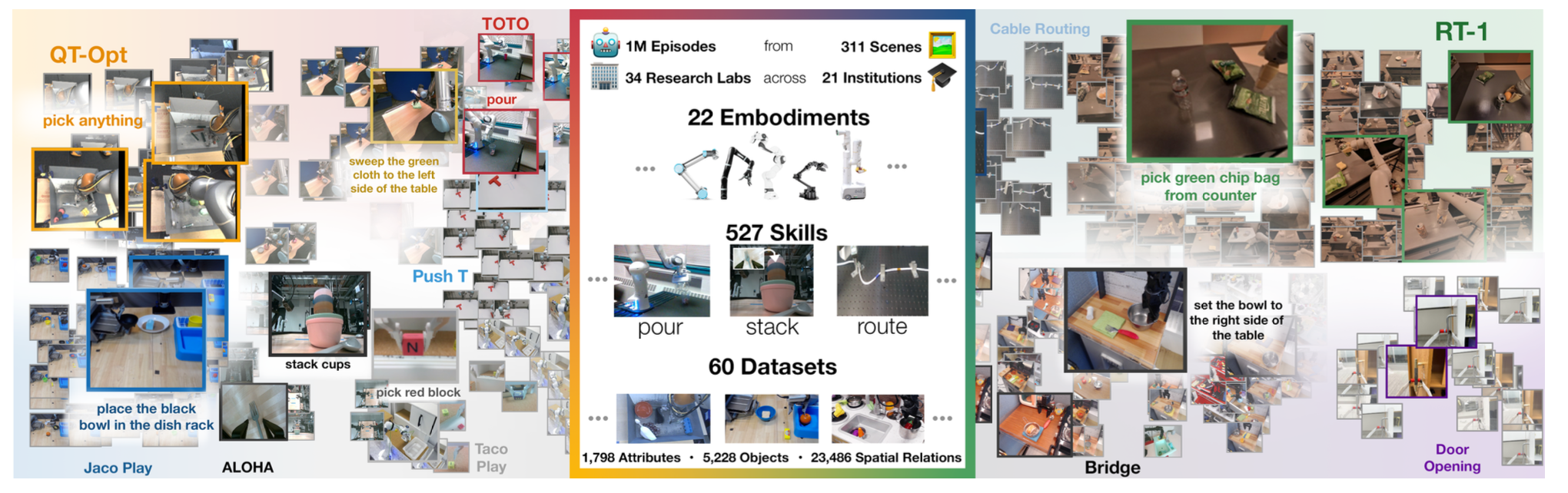
Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models
A. Padalkar, et al.
@ CoRL 2023

RT-2: Vision-Language-Action Models Transfer Web Knowledge to Robotic Control
A. Brohan, N. Brown, J. Carbajal, Y. Chebotar, X. Chen, K. Choromanski, T. Ding, D. Driess, A. Dubey, C. Finn, P. Florence, C. Fu, M. Gonzalez Arenas, K. Gopalakrishnan, K. Han, K. Hausman, A. Herzog, J. Hsu, B. Ichter, A. Irpan, N. Joshi, R. Julian, D. Kalashnikov, Y. Kuang, I. Leal, L. Lee, T. E. Lee, S. Levine, Y. Lu, H. Michalewski, I. Mordatch, K. Pertsch, K. Rao, K. Reymann, M. Ryoo, G. Salazar, P. Sanketi, P. Sermanet, J. Singh, A. Singh, R. Soricut, H. Tran, V. Vanhoucke, Q. Vuong, A. Wahid, S. Welker, P. Wohlhart, J. Wu, F. Xia, T. Xiao, P. Xu, S. Xu, T. Yu, B. Zitkovich
@ CoRL 2023

PaLM-E: An Embodied Multimodal Language Model
Danny Driess, Fei Xia, Mehdi S. M. Sajjadi, Corey Lynch, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Brian Ichter, Ayzaan Wahid, Jonathan Tompson, Quan Vuong, Tianhe Yu, Wenlong Huang, Yevgen Chebotar, Pierre Sermanet, Daniel Duckworth, Sergey Levine, Vincent Vanhoucke, Karol Hausman, Marc Toussaint, Klaus Greff, Andy Zeng, Igor Mordatch, Pete Florence
@ ICML 2023

Inner Monologue: Embodied Reasoning through Planning with Language Models
Wenlong Huang*, Fei Xia*, Ted Xiao*, Harris Chan, Jacky Liang, Pete Florence, Andy Zeng, Jonathan Tompson, Igor Mordatch, Yevgen Chebotar, Pierre Sermanet, Noah Brown, Tomas Jackson, Linda Luu, Sergey Levine, Karol Hausman, Brian Ichter.
@ CoRL 2022

(SayCan) Do As I Can, Not As I Say: Grounding Language in Robotic Affordances
M. Ahn, A. Brohan, N. Brown, Y. Chebotar, O. Cortes, B. David, C. Fu, Ch. Finn, K. Gopalakrishnan, K. Hausman, A. Herzog, D. Ho, J. Hsu, J. Ibarz, B. Ichter, A. Irpan, E. Jang, R. Jauregui Ruano, K. Jeffrey, S. Jesmonth, N. J Joshi, R. Julian, D. Kalashnikov, Y. Kuang, K.-H. Lee, S. Levine, Y. Lu, L. Luu, C. Parada, P. Pastor, J. Quiambao, K. Rao, J. Rettinghouse, D. Reyes, P. Sermanet, N. Sievers, Cl. Tan, A. Toshev, V. Vanhoucke, F. Xia (co-corresponding author), T. Xiao, P. Xu, S. Xu, M. Yan, A. Zeng (alphebatically listed)
@ CoRL 2022
Grounding Language in Play
Corey Lynch and Pierre Sermanet @ RSS 2021
We present a simple and scalable approach for controlling robots with natural language: play through teleoperation, then answer “how do I go from start to finish?” for random episodes. We can then type in commands in real time.
By hooking up our English-trained model with a pre-trained language embedding trained on lots of text and different languages, it not only improves control but also allows commanding the model in 16 languages.
Combining natural language with play provides a breadth of skills while having no tasks determined in advance. This yields flexible specification of tasks, for example we can compose tasks on the fly: “pick up the object”, then “put the object in the trash”.
Learning Latent Plans from Play
Corey Lynch, Mohi Khansari, Ted Xiao, Vikash Kumar, Jonathan Tompson, Sergey Levine, Pierre Sermanet @ CoRL 2019
How to scale-up multi-task learning?
Self-supervise plan representations from lots of cheap unlabeled play data (no RL was used).

Self-Supervised Actionable Representations
Debidatta Dwibedi, Jonathan Tompson, Corey Lynch, Pierre Sermanet @ IROS 2018
We learn continuous control entirely from raw pixels.
We use a multi-frame TCN to self-supervise task-agnostic representations from vision only, using 2 slightly different views of the cheetah.
Then using RL on top of our embeddings we learn the cheetah task almost as well as if we were using the true proprioceptive states of the cheetah.
Time-Contrastive Networks (TCN)
Pierre Sermanet, Corey Lynch, Yevgen Chebotar, Jasmine Hsu, Eric Jang, Stefan Schaal, Sergey Levine @ ICRA 2018
We propose a general self-supervised method for learning representations from raw unlabeled videos.
We show that the self-supervised representations are rich enough to perform robotic tasks.
We use the distance in our learned embedding space to a video demonstration as a reward. An RL algorithm can learn to perform a pouring task using this reward.
The robot has learned to pour in only 9 iterations using a single video demonstration, while never receiving any labels.
We also show that a robot can teach itself how to imitate people: by training a single TCN on videos of both humans and robots peforming random motions, the TCN model is able to find correspondences between humans and robots, despite never being given any label correspondences.

Unsupervised Perceptual Rewards
Pierre Sermanet, Kelvin Xu, Sergey Levine @ RSS 2017
We propose learning unsupervised perceptual rewards that can be fed to an RL system and show it is able to learn a robotic task such as door opening from a few human demonstrations.
Visual Attention
Pierre Sermanet, Andrea Frome, Esteban Real @ ICLR 2015 (workshop)
We demonstrate a foveated attention RNN that is able to perform fine-grained classification.
Tracking naturally emerges from our fovated model when ran on videos, even though it was only trained on still images.


Inception / GoogLeNet
Christian Szegedy, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent Vanhoucke, Andrew Rabinovich @ CVPR 2015
A deep architecture for computer vision. Our model obtained 1st place for the classification and detection tasks in the 2014 ImageNet Challenge.

Dogs vs. Cats Kaggle challenge
Pierre Sermanet (2014)
1st place in an image classification Kaggle challenge between dog and cat images. Most of the top entries are based on our OverFeat model.


OverFeat
Pierre Sermanet, David Eigen, Xiang Zhang, Michael Mathieu, Rob Fergus, Yann LeCun @ ICLR 2014
This model obtained 1st place in the 2013 ImageNet object localization challenge. The model and pre-trained features were later released to the public.
Overfeat has been used by Apple for on-device face detection in iPhones: blogpost
Pedestrian Detection
Pierre Sermanet, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Soumith Chintala, Yann Lecun @ CVPR 2013
State of the art results on pedestrian detection datasets using deep ConvNets in the EBLearn framework.

Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to House Numbers Digit Classification
Pierre Sermanet, Soumith Chintala, Yann LeCun @ ICPR 2012
State of the art results in house numbers classification using deep ConvNets.


Traffic Sign Recognition
Pierre Sermanet, Yann LeCun @ IJCNN 2011
This deep model obtained 2nd place in a traffic sign recognition challenge using the EBLearn framework. It uses skip connections in deep ConvNets to better combine low-lvel and high-level learned features.

Unsupervised Convolutional Feature Hierarchies
Koray Kavukcuoglu, Pierre Sermanet, Y-Lan Boureau, Karol Gregor, Michael Mathieu, Yann LeCun @ NIPS 2010
An unsupervised method for learning multi-stage hierarchies of sparse convolutional features. One of the few instances of this period where unsupervised pretraining improved results in a supervised task.


EBLearn
Pierre Sermanet, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Yann LeCun @ ICTAI 2009
Additional help from Soumith Chintala.
A C++ deep learning framework similar to Torch and used for multiple state of the art results in computer vision.
Teaching Assitant for NYU Robotics class
Pierre Sermanet, Yann LeCun (2009)
LAGR: Learning Applied to Ground Robots
Yann LeCun, Urs Muller, Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Chris Crudelle, Beat Flepp, Ayse Erkan, Matt Grimes, Raia Hadsell, Koray Kavakcuoglu, Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, Jan Ben, Sumit Chopra, Jeff Han, Marc Peyote, Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, Ilya Rosenberg, Yury Sulsky
A DARPA challenge where the NYU-NetScale team developed ConvNets for long-range off-road navigation from 2004 to 2008.
Learning Long-Range Vision for Autonomous Off-Road Driving
Raia Hadsell, Pierre Sermanet, Jan Ben, Ayse Erkan, Marco Scoffier, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ JFR 2009
An overview paper of our self-supervised deep learning vision model.
Collision-Free Off-Road Robot Navigation
Pierre Sermanet, Raia Hadsell, Marco Scoffier, Matt Grimes, Jan Ben, Ayse Erkan, Chris Crudele, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ JFR 2009
An overview paper of our navigation system designed to naturally handle errors and outputs coming out of a deep vision model. This model decouples the fast and short-range navigation from the slow and long-range navigation to achieve robustness.

Learning Maneuver Dictionaries for Ground Robot Planning
Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Chris Crudele, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ ISR 2008
Instead of computing the theoretical dynamics of a vehicle, we propose to simply record the observed dynamics while a human operator "plays" with the robot, essentially trying all possible moves. At test time, the model has a bank of observed possible trajectories for every state of the motors. Trajectories leading to collisions are discarded, while the fastest available trajectory is selected. While we observed many collisions using the baseline system, we did not observe collisions after introducing this model.
Mapping and Planning under Uncertainty in Mobile Robots with Long-Range Perception
Pierre Sermanet, Raia Hadsell, Marco Scoffier, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ IROS 2008
A hyperbolic-polar coordinate mapping system that is naturally suited to handle imprecisions in long-range visual navigation.

Deep Belief Net Learning in a Long-Range Vision System
Raia Hadsell, Ayse Erkan, Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ IROS 2008
Self-supervised long-range visual navigation with deep ConvNets.

Online Learning for Offroad Robots
Raia Hadsell, Pierre Sermanet, Ayse Naz Erkan, Jan Ben, Jefferson Han, Beat Flepp, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ RSS 2007
Online adaptation of long-range vision by self-supervising with short-range stereo vision.
EUROBOT 2004 Competition
Computer vision, navigation and behaviors by Pierre Sermanet, Philippe Rambert, Jean-Baptiste Mouret
Entire team: Evolutek
Vision-based behaviors in a robot-rugby challenge.
Machine Learning for Robotics / Vision / Language / Actions / Safety
Selected highlights
| 2025 | 100k citations across machine learning, computer vision, and robotics + Laws of robotics generated from images and sci-fi + CVPR Prize for 10-year significant impact on computer vision by GoogLeNet paper |
| 2023 | Open-sourced large-scale VQA benchmark for robotics and developped embodied long-horizon reasoning |
| 2020 | First manipulation VLA: end-to-end Vision-Language-Action models for robotic manipulation and learned from unstructured play videos and very few labels |
| 2017 | Fully self-supervised imitation from video → robot policy learned without any labels |
| 2016 | Founding member of Google Brain Robotics team + Unsupervised rewards from vision |
| 2014 | Winner of Dogs vs Cats and 2014 ImageNet competitions + Joined Google Brain |
| 2013 | PhD graduation with Yann LeCun @ New York University + Open-sourced one of the first deep vision models (OverFeat) + Winner of 2013 ImageNet competition |
| 2010 - 2012 | ConvNets for detection, classification and unsupervised representations |
| 2009 | Designed and released an early open-source deep learning framework (EBLearn) |
| 2006 | Proposed a fast & slow thinking architecture for robotics (system 1 / system 2) |
| 2005 | Deep learning for robotics in DARPA’s LAGR program |

|
SciFi-Benchmark: Leveraging Science Fiction To Improve Robot Behavior
Pierre Sermanet, Anirudha Majumdar, Vikas Sindhwani Q: How would AI-powered robots behave if dropped into Science Fiction literature? A: 95.8% aligned with humans (Sci-Fi decisions are only 21.2% aligned). Q: Can we generate useful robot constitutions 📜 from Sci-Fi? A: Sci-Fi inspired constitutions yield some of the strongest alignment on realistic safety benchmarks. |
|

|
Generating Robot Constitutions
& Benchmarks for Semantic Safety Pierre Sermanet, Anirudha Majumdar, Alex Irpan, Dmitry Kalashnikov, Vikas Sindhwani Q: How can we ensure robots behave properly at scale? A: Robot constitutions 📜! Q: How do we verify behavior in undesirable situations at scale? A: Generation! We release the ASIMOV Benchmark for Semantic Safety of robots. We generate difficult-to-capture undesirable situations using image generation. We also generate robot constitutions straight from images. |
|
|
RoboVQA: Multimodal Long-Horizon Reasoning for Robotics
Pierre Sermanet, Tianli Ding, Jeffrey Zhao, Fei Xia, Yuan Cao et al. @ ICRA 2024, 2023 CoRL and NeurIPS workshops Need help in the real world? RoboVQA can guide robots and humans through long-horizon tasks on a phone via Google Meet. We propose scalable real-world data acquisition and augmentation strategies and release a dataset of 800k (video, question/answer) with robots & humans doing various long-horizon tasks. We train a small video model (380M) that outperforms large state of the art zero-shot models by ~2x and demonstrate that scalable strategies for acquiring new data remains criticial. We use a speech intervention mechanism that automatically quantifies progress (intervention rate), provides corrections to retrain on, and allows performing tasks to completion in supervised real-world deployment. |
||

|
Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models
A. Padalkar, et al. @ CoRL 2023 |
|

|
RT-2: Vision-Language-Action Models Transfer Web Knowledge to Robotic Control
A. Brohan, N. Brown, J. Carbajal, Y. Chebotar, X. Chen, K. Choromanski, T. Ding, D. Driess, A. Dubey, C. Finn, P. Florence, C. Fu, M. Gonzalez Arenas, K. Gopalakrishnan, K. Han, K. Hausman, A. Herzog, J. Hsu, B. Ichter, A. Irpan, N. Joshi, R. Julian, D. Kalashnikov, Y. Kuang, I. Leal, L. Lee, T. E. Lee, S. Levine, Y. Lu, H. Michalewski, I. Mordatch, K. Pertsch, K. Rao, K. Reymann, M. Ryoo, G. Salazar, P. Sanketi, P. Sermanet, J. Singh, A. Singh, R. Soricut, H. Tran, V. Vanhoucke, Q. Vuong, A. Wahid, S. Welker, P. Wohlhart, J. Wu, F. Xia, T. Xiao, P. Xu, S. Xu, T. Yu, B. Zitkovich @ CoRL 2023 |
|

|
PaLM-E: An Embodied Multimodal Language Model
Danny Driess, Fei Xia, Mehdi S. M. Sajjadi, Corey Lynch, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Brian Ichter, Ayzaan Wahid, Jonathan Tompson, Quan Vuong, Tianhe Yu, Wenlong Huang, Yevgen Chebotar, Pierre Sermanet, Daniel Duckworth, Sergey Levine, Vincent Vanhoucke, Karol Hausman, Marc Toussaint, Klaus Greff, Andy Zeng, Igor Mordatch, Pete Florence @ ICML 2023 |
|

|
Inner Monologue: Embodied Reasoning through Planning with Language Models
Wenlong Huang*, Fei Xia*, Ted Xiao*, Harris Chan, Jacky Liang, Pete Florence, Andy Zeng, Jonathan Tompson, Igor Mordatch, Yevgen Chebotar, Pierre Sermanet, Noah Brown, Tomas Jackson, Linda Luu, Sergey Levine, Karol Hausman, Brian Ichter. @ CoRL 2022 |
|

|
(SayCan) Do As I Can, Not As I Say: Grounding Language in Robotic Affordances
M. Ahn, A. Brohan, N. Brown, Y. Chebotar, O. Cortes, B. David, C. Fu, Ch. Finn, K. Gopalakrishnan, K. Hausman, A. Herzog, D. Ho, J. Hsu, J. Ibarz, B. Ichter, A. Irpan, E. Jang, R. Jauregui Ruano, K. Jeffrey, S. Jesmonth, N. J Joshi, R. Julian, D. Kalashnikov, Y. Kuang, K.-H. Lee, S. Levine, Y. Lu, L. Luu, C. Parada, P. Pastor, J. Quiambao, K. Rao, J. Rettinghouse, D. Reyes, P. Sermanet, N. Sievers, Cl. Tan, A. Toshev, V. Vanhoucke, F. Xia (co-corresponding author), T. Xiao, P. Xu, S. Xu, M. Yan, A. Zeng (alphebatically listed) @ CoRL 2022 |
|
|
Grounding Language in Play
Corey Lynch and Pierre Sermanet @ RSS 2021 We present a simple and scalable approach for controlling robots with natural language: play through teleoperation, then answer “how do I go from start to finish?” for random episodes. We can then type in commands in real time. By hooking up our English-trained model with a pre-trained language embedding trained on lots of text and different languages, it not only improves control but also allows commanding the model in 16 languages. Combining natural language with play provides a breadth of skills while having no tasks determined in advance. This yields flexible specification of tasks, for example we can compose tasks on the fly: “pick up the object”, then “put the object in the trash”. |
||
|
Learning Latent Plans from Play
Corey Lynch, Mohi Khansari, Ted Xiao, Vikash Kumar, Jonathan Tompson, Sergey Levine, Pierre Sermanet @ CoRL 2019 How to scale-up multi-task learning? Self-supervise plan representations from lots of cheap unlabeled play data (no RL was used). |
||

|
Self-Supervised Actionable Representations
Debidatta Dwibedi, Jonathan Tompson, Corey Lynch, Pierre Sermanet @ IROS 2018 We learn continuous control entirely from raw pixels. We use a multi-frame TCN to self-supervise task-agnostic representations from vision only, using 2 slightly different views of the cheetah. Then using RL on top of our embeddings we learn the cheetah task almost as well as if we were using the true proprioceptive states of the cheetah. |
|
|
Time-Contrastive Networks (TCN)
Pierre Sermanet, Corey Lynch, Yevgen Chebotar, Jasmine Hsu, Eric Jang, Stefan Schaal, Sergey Levine @ ICRA 2018 We propose a general self-supervised method for learning representations from raw unlabeled videos. We show that the self-supervised representations are rich enough to perform robotic tasks. We use the distance in our learned embedding space to a video demonstration as a reward. An RL algorithm can learn to perform a pouring task using this reward. The robot has learned to pour in only 9 iterations using a single video demonstration, while never receiving any labels. We also show that a robot can teach itself how to imitate people: by training a single TCN on videos of both humans and robots peforming random motions, the TCN model is able to find correspondences between humans and robots, despite never being given any label correspondences. |
||

|
Unsupervised Perceptual Rewards
Pierre Sermanet, Kelvin Xu, Sergey Levine @ RSS 2017 We propose learning unsupervised perceptual rewards that can be fed to an RL system and show it is able to learn a robotic task such as door opening from a few human demonstrations. |
|
|
Visual Attention
Pierre Sermanet, Andrea Frome, Esteban Real @ ICLR 2015 (workshop) We demonstrate a foveated attention RNN that is able to perform fine-grained classification. Tracking naturally emerges from our fovated model when ran on videos, even though it was only trained on still images. |
||

|
Inception / GoogLeNet
Christian Szegedy, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent Vanhoucke, Andrew Rabinovich @ CVPR 2015 A deep architecture for computer vision. Our model obtained 1st place for the classification and detection tasks in the 2014 ImageNet Challenge. |
|

|
Dogs vs. Cats Kaggle challenge
Pierre Sermanet (2014) 1st place in an image classification Kaggle challenge between dog and cat images. Most of the top entries are based on our OverFeat model. |
|


|
OverFeat
Pierre Sermanet, David Eigen, Xiang Zhang, Michael Mathieu, Rob Fergus, Yann LeCun @ ICLR 2014 This model obtained 1st place in the 2013 ImageNet object localization challenge. The model and pre-trained features were later released to the public. Overfeat has been used by Apple for on-device face detection in iPhones: blogpost |
|
|
Pedestrian Detection
Pierre Sermanet, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Soumith Chintala, Yann Lecun @ CVPR 2013 State of the art results on pedestrian detection datasets using deep ConvNets in the EBLearn framework. |
||

|
Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to House Numbers Digit Classification
Pierre Sermanet, Soumith Chintala, Yann LeCun @ ICPR 2012 State of the art results in house numbers classification using deep ConvNets. |
|
 
|
Traffic Sign Recognition
Pierre Sermanet, Yann LeCun @ IJCNN 2011 This deep model obtained 2nd place in a traffic sign recognition challenge using the EBLearn framework. It uses skip connections in deep ConvNets to better combine low-lvel and high-level learned features. |
|

|
Unsupervised Convolutional Feature Hierarchies
Koray Kavukcuoglu, Pierre Sermanet, Y-Lan Boureau, Karol Gregor, Michael Mathieu, Yann LeCun @ NIPS 2010 An unsupervised method for learning multi-stage hierarchies of sparse convolutional features. One of the few instances of this period where unsupervised pretraining improved results in a supervised task. |
|


|
EBLearn
Pierre Sermanet, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Yann LeCun @ ICTAI 2009 Additional help from Soumith Chintala. A C++ deep learning framework similar to Torch and used for multiple state of the art results in computer vision. |
|
|
Teaching Assitant for NYU Robotics class
Pierre Sermanet, Yann LeCun (2009) |
||
|
LAGR: Learning Applied to Ground Robots
Yann LeCun, Urs Muller, Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Chris Crudelle, Beat Flepp, Ayse Erkan, Matt Grimes, Raia Hadsell, Koray Kavakcuoglu, Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, Jan Ben, Sumit Chopra, Jeff Han, Marc Peyote, Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, Ilya Rosenberg, Yury Sulsky A DARPA challenge where the NYU-NetScale team developed ConvNets for long-range off-road navigation from 2004 to 2008. |
||
|
Learning Long-Range Vision for Autonomous Off-Road Driving
Raia Hadsell, Pierre Sermanet, Jan Ben, Ayse Erkan, Marco Scoffier, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ JFR 2009 An overview paper of our self-supervised deep learning vision model. |
||
|
Collision-Free Off-Road Robot Navigation
Pierre Sermanet, Raia Hadsell, Marco Scoffier, Matt Grimes, Jan Ben, Ayse Erkan, Chris Crudele, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ JFR 2009 An overview paper of our navigation system designed to naturally handle errors and outputs coming out of a deep vision model. This model decouples the fast and short-range navigation from the slow and long-range navigation to achieve robustness. |
||

|
Learning Maneuver Dictionaries for Ground Robot Planning
Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Chris Crudele, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ ISR 2008 Instead of computing the theoretical dynamics of a vehicle, we propose to simply record the observed dynamics while a human operator "plays" with the robot, essentially trying all possible moves. At test time, the model has a bank of observed possible trajectories for every state of the motors. Trajectories leading to collisions are discarded, while the fastest available trajectory is selected. While we observed many collisions using the baseline system, we did not observe collisions after introducing this model. |
|
|
Mapping and Planning under Uncertainty in Mobile Robots with Long-Range Perception
Pierre Sermanet, Raia Hadsell, Marco Scoffier, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ IROS 2008 A hyperbolic-polar coordinate mapping system that is naturally suited to handle imprecisions in long-range visual navigation. |
||

|
Deep Belief Net Learning in a Long-Range Vision System
Raia Hadsell, Ayse Erkan, Pierre Sermanet, Marco Scoffier, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ IROS 2008 Self-supervised long-range visual navigation with deep ConvNets. |
|

|
Online Learning for Offroad Robots
Raia Hadsell, Pierre Sermanet, Ayse Naz Erkan, Jan Ben, Jefferson Han, Beat Flepp, Urs Muller, Yann LeCun @ RSS 2007 Online adaptation of long-range vision by self-supervising with short-range stereo vision. |
|
|
EUROBOT 2004 Competition
Computer vision, navigation and behaviors by Pierre Sermanet, Philippe Rambert, Jean-Baptiste Mouret Entire team: Evolutek Vision-based behaviors in a robot-rugby challenge. |
||